07: Data Import with Tidyverse
Before we begin
- If you are not using Workbench, please install the following packages:
- The command will install a large set of packages that are designed to work together, including ggplot2.
And load the package
Credit
- This presentation is heavily influenced by Rafael Irizarry’s book Introduction to Data Science and his corresponding course on EdX.
- It also draws on material from previous MPI R courses given by Devon Ryan and David Koppstein.
- Updated with the Software Carpentry course “Introduction to data analysis with R and Bioconductor”



Following along
For each module, please create a separate R script and type in and execute the commands that are to follow along.
The code from some slides depends on the previous slides!
You can execute each line individually using Command-Enter on Mac, alt-Enter on Workbench.
Our example dataset
Gender matched eight week old C57BL/6 mice were inoculated saline or with Influenza A (Puerto Rico/8/34; PR8, 1.0 HAU) by intranasal route and transcriptomic changes in the cerebellum and spinal cord tissues were evaluated by RNA-seq (Hiseq-2500 100bp PE-reads) at days 0 (non-infected), 4 and 8.
But for this session, we’ll use https://raw.githubusercontent.com/maxplanck-ie/Rintro/refs/heads/2025.04/qmd/data/rnaseq_counts_wide.csv which contains a table for gene expression (1474 genes) per sample (22 samples)
Blackmore S, et al. Influenza infection triggers disease in a genetic model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.PNAS 2017,114(30):E6107-E6116. PMID: 28696309
Data Import in the Tidyverse
The first step for any analysis is importing the data into a machine-readable format. The tidyverse offers the readr:: and readxl:: packages.
Note:
most data can be easy to import when it’s properly formatted in a text format
MS Excel files can be read and/or write but should be avoided
Table formats
CSV (comma separated values)
sample,sex,age,treatment,response
A001,M,8,KO,5200
A002,M,4,WT,4430
A003,F,4,KO,344
B001,F,6,WT,2328TSV (tab separated values)
sample\tsex\tage\ttreatment\tresponse
A001\tM\t8\tKO\t5200
A002\tM\t4\tWT\t4430
A003\tF\t4\tKO\t344
B001\tF\t6t\tWT\t2328readr::
readr::is the Tidyverse library for reading data from text formats.read_csv(),read_tsv(),read_table(), andread_delim()are some of the functions providedread_csv2()allows for reading of European-style CSV files (e.g. using;)
readr:: in action
Example commands, don’t run
readr:: in action
rna_file = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/maxplanck-ie/Rintro/refs/heads/2025.04/qmd/data/rnaseq_counts_wide.csv"
rna = read_csv(rna_file)
# What is this "*rna*"?
rna # A tibble: 1,474 × 23
gene GSM2545336 GSM2545337 GSM2545338 GSM2545339 GSM2545340 GSM2545341
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Asl 1170 361 400 586 626 988
2 Apod 36194 10347 9173 10620 13021 29594
3 Cyp2d22 4060 1616 1603 1901 2171 3349
4 Klk6 287 629 641 578 448 195
5 Fcrls 85 233 244 237 180 38
6 Slc2a4 782 231 248 265 313 786
7 Exd2 1619 2288 2235 2513 2366 1359
8 Gjc2 288 595 568 551 310 146
9 Plp1 43217 101241 96534 58354 53126 27173
10 Gnb4 1071 1791 1867 1430 1355 798
# ℹ 1,464 more rows
# ℹ 16 more variables: GSM2545342 <dbl>, GSM2545343 <dbl>, GSM2545344 <dbl>,
# GSM2545345 <dbl>, GSM2545346 <dbl>, GSM2545347 <dbl>, GSM2545348 <dbl>,
# GSM2545349 <dbl>, GSM2545350 <dbl>, GSM2545351 <dbl>, GSM2545352 <dbl>,
# GSM2545353 <dbl>, GSM2545354 <dbl>, GSM2545362 <dbl>, GSM2545363 <dbl>,
# GSM2545380 <dbl>What is a tibble?
- Tibbles are like data frames, but more modern, and are built for the Tidyverse
- The interface is the same, using e.g.
$for columns - Tibbles can contain more complex objects than just strings, numbers, or booleans, like lists or functions
- Tibbles can be grouped
- You can see the types of each column in a tibble
What is Tidy Data?
- In tidy data, each row is an observation and each column is a different variable (long-format).
- In wide data, each row contains several observations, and the columns contain values (wide-format).

Hands on
Get the basic statistics for each sample in rna
Which sample has the highest mean expression?
Hands on
gene GSM2545336 GSM2545337 GSM2545338
Length:1474 Min. : 0 Min. : 0.00 Min. : 0
Class :character 1st Qu.: 91 1st Qu.: 56.25 1st Qu.: 52
Mode :character Median : 611 Median : 494.50 Median : 468
Mean : 2062 Mean : 1765.51 Mean : 1668
3rd Qu.: 2090 3rd Qu.: 1798.75 3rd Qu.: 1692
Max. :89445 Max. :101241.00 Max. :96534
GSM2545339 GSM2545340 GSM2545341 GSM2545342
Min. : 0.00 Min. : 0.0 Min. : 0 Min. : 0.0
1st Qu.: 77.25 1st Qu.: 59.5 1st Qu.: 47 1st Qu.: 63.0
Median : 541.50 Median : 487.0 Median : 462 Median : 470.5
Mean : 1696.12 Mean : 1681.8 Mean : 1638 Mean : 1594.1
3rd Qu.: 1772.75 3rd Qu.: 1811.5 3rd Qu.: 1694 3rd Qu.: 1625.8
Max. :58354.00 Max. :53126.0 Max. :61758 Max. :60132.0
GSM2545343 GSM2545344 GSM2545345 GSM2545346
Min. : 0.00 Min. : 0.0 Min. : 0.0 Min. : 0.00
1st Qu.: 72.25 1st Qu.: 58.0 1st Qu.: 52.0 1st Qu.: 67.25
Median : 634.00 Median : 502.5 Median : 497.5 Median : 497.50
Mean : 2106.96 Mean : 1712.4 Mean : 1700.2 Mean : 1692.77
3rd Qu.: 2266.25 3rd Qu.: 1778.2 3rd Qu.: 1834.5 3rd Qu.: 1722.25
Max. :98658.00 Max. :61356.0 Max. :61647.0 Max. :71706.00
GSM2545347 GSM2545348 GSM2545349 GSM2545350
Min. : 0.0 Min. : 0.00 Min. : 0 Min. : 0.00
1st Qu.: 63.0 1st Qu.: 70.25 1st Qu.: 66 1st Qu.: 71.25
Median : 549.5 Median : 570.50 Median : 573 Median : 624.00
Mean : 1805.4 Mean : 1976.72 Mean : 1871 Mean : 2208.66
3rd Qu.: 1872.0 3rd Qu.: 2038.00 3rd Qu.: 2009 3rd Qu.: 2314.75
Max. :71375.0 Max. :102790.00 Max. :82722 Max. :91642.00
GSM2545351 GSM2545352 GSM2545353 GSM2545354
Min. : 0.0 Min. : 0.00 Min. : 0 Min. : 0
1st Qu.: 83.0 1st Qu.: 84.25 1st Qu.: 74 1st Qu.: 60
Median : 557.5 Median : 647.00 Median : 606 Median : 534
Mean : 1887.7 Mean : 2181.93 Mean : 2004 Mean : 1823
3rd Qu.: 1885.2 3rd Qu.: 2294.00 3rd Qu.: 2149 3rd Qu.: 1961
Max. :75277.0 Max. :74044.00 Max. :71237 Max. :84540
GSM2545362 GSM2545363 GSM2545380
Min. : 0.00 Min. : 0 Min. : 0.00
1st Qu.: 93.25 1st Qu.: 48 1st Qu.: 75.25
Median : 625.00 Median : 520 Median : 597.50
Mean : 1976.61 Mean : 1816 Mean : 2059.77
3rd Qu.: 1956.25 3rd Qu.: 1997 3rd Qu.: 2071.25
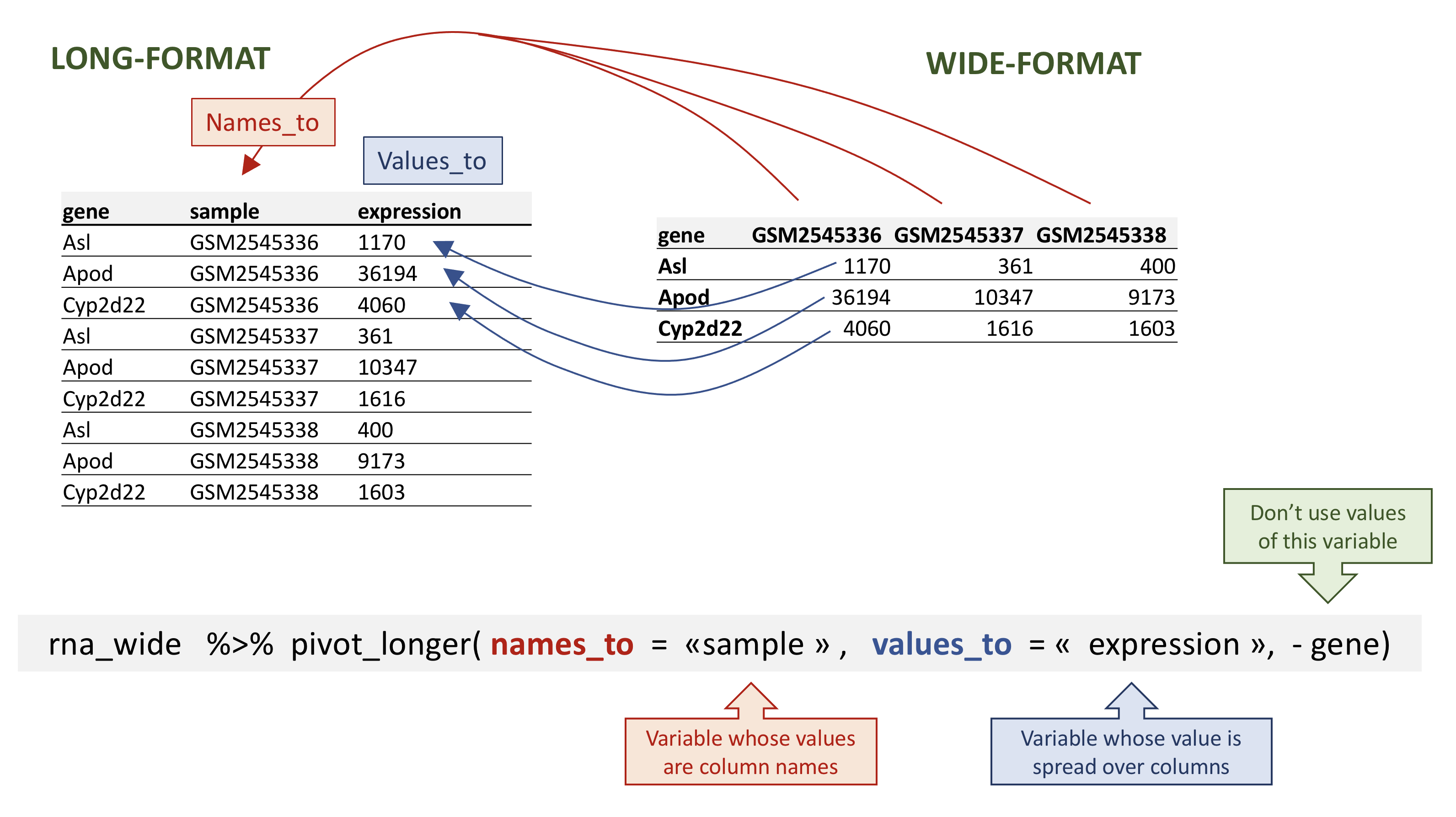
Max. :71380.00 Max. :66033 Max. :87942.00 Dplyr in action - pivot_longer()
To transform the data in a long-format we use pivot_longer(), it takes as inputs:
- the
datato be transformed; - the
names_tothe new column name we wish to create and populate with the current column names; - the
values_tothe new column name we wish to create and populate with current values; - the names of the columns to be used to populate the
names_toandvalues_tovariables (or to drop with-).
Dplyr in action - pivot_longer()
# A tibble: 32,428 × 3
gene sample expression
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 Asl GSM2545336 1170
2 Asl GSM2545337 361
3 Asl GSM2545338 400
4 Asl GSM2545339 586
5 Asl GSM2545340 626
6 Asl GSM2545341 988
7 Asl GSM2545342 836
8 Asl GSM2545343 535
9 Asl GSM2545344 586
10 Asl GSM2545345 597
# ℹ 32,418 more rowsDplyr in action - pivot_longer()
Dplyr in action - pivot_longer()
Column selection can be defined with patterns
rna_long2 = pivot_longer(
rna,
names_to = "sample",
values_to = "expression",
cols = starts_with("GSM"))
rna_long2# A tibble: 32,428 × 3
gene sample expression
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 Asl GSM2545336 1170
2 Asl GSM2545337 361
3 Asl GSM2545338 400
4 Asl GSM2545339 586
5 Asl GSM2545340 626
6 Asl GSM2545341 988
7 Asl GSM2545342 836
8 Asl GSM2545343 535
9 Asl GSM2545344 586
10 Asl GSM2545345 597
# ℹ 32,418 more rowsDplyr in action - pivot_longer()
Column selection can be also defined with ranges
rna_long3 = pivot_longer(
rna,
names_to = "sample",
values_to = "expression",
GSM2545336:GSM2545380)
rna_long3# A tibble: 32,428 × 3
gene sample expression
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 Asl GSM2545336 1170
2 Asl GSM2545337 361
3 Asl GSM2545338 400
4 Asl GSM2545339 586
5 Asl GSM2545340 626
6 Asl GSM2545341 988
7 Asl GSM2545342 836
8 Asl GSM2545343 535
9 Asl GSM2545344 586
10 Asl GSM2545345 597
# ℹ 32,418 more rowsDplyr in action - pivot_wider()
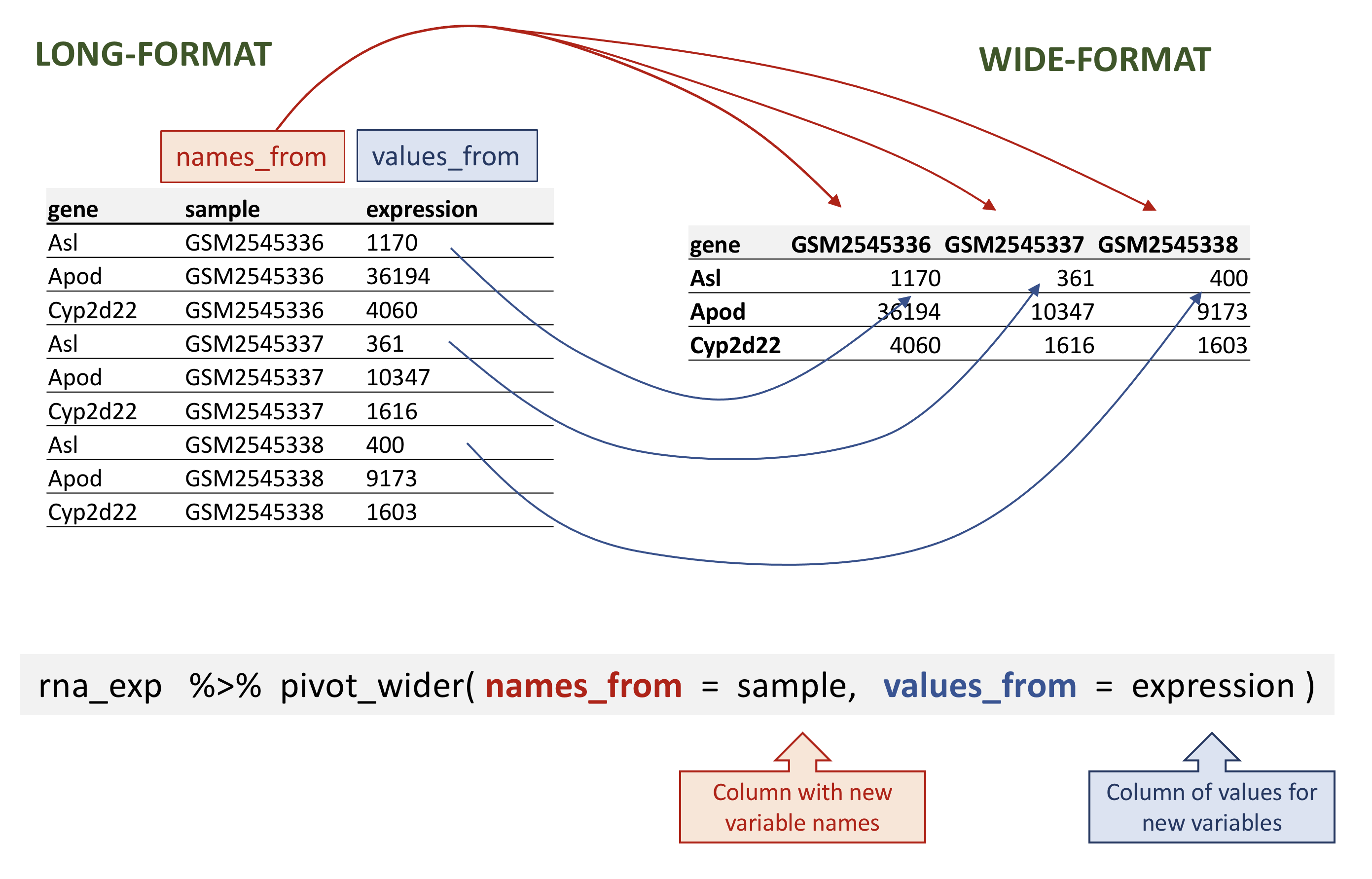
The inverse operation is pivot_wider() can transform long-format to wide-format.
It takes three main arguments:
the
datato be transformedthe
names_fromare the column whose values will become new column namesthe
values_fromare the column whose values will fill the new columns
Dplyr in action - pivot_wider()
# A tibble: 1,474 × 23
gene GSM2545336 GSM2545337 GSM2545338 GSM2545339 GSM2545340 GSM2545341
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Asl 1170 361 400 586 626 988
2 Apod 36194 10347 9173 10620 13021 29594
3 Cyp2d22 4060 1616 1603 1901 2171 3349
4 Klk6 287 629 641 578 448 195
5 Fcrls 85 233 244 237 180 38
6 Slc2a4 782 231 248 265 313 786
7 Exd2 1619 2288 2235 2513 2366 1359
8 Gjc2 288 595 568 551 310 146
9 Plp1 43217 101241 96534 58354 53126 27173
10 Gnb4 1071 1791 1867 1430 1355 798
# ℹ 1,464 more rows
# ℹ 16 more variables: GSM2545342 <dbl>, GSM2545343 <dbl>, GSM2545344 <dbl>,
# GSM2545345 <dbl>, GSM2545346 <dbl>, GSM2545347 <dbl>, GSM2545348 <dbl>,
# GSM2545349 <dbl>, GSM2545350 <dbl>, GSM2545351 <dbl>, GSM2545352 <dbl>,
# GSM2545353 <dbl>, GSM2545354 <dbl>, GSM2545362 <dbl>, GSM2545363 <dbl>,
# GSM2545380 <dbl>Dplyr in action - pivot_wider()
Dplyr in action - pivot_wider()
By default, missing values will be converted to NA, we can change it with values_fill
rna_wide_noNAs = pivot_wider(
rna_long,
names_from = sample,
values_from = expression,
values_fill = 0)
rna_wide_noNAs# A tibble: 1,474 × 23
gene GSM2545336 GSM2545337 GSM2545338 GSM2545339 GSM2545340 GSM2545341
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Asl 1170 361 400 586 626 988
2 Apod 36194 10347 9173 10620 13021 29594
3 Cyp2d22 4060 1616 1603 1901 2171 3349
4 Klk6 287 629 641 578 448 195
5 Fcrls 85 233 244 237 180 38
6 Slc2a4 782 231 248 265 313 786
7 Exd2 1619 2288 2235 2513 2366 1359
8 Gjc2 288 595 568 551 310 146
9 Plp1 43217 101241 96534 58354 53126 27173
10 Gnb4 1071 1791 1867 1430 1355 798
# ℹ 1,464 more rows
# ℹ 16 more variables: GSM2545342 <dbl>, GSM2545343 <dbl>, GSM2545344 <dbl>,
# GSM2545345 <dbl>, GSM2545346 <dbl>, GSM2545347 <dbl>, GSM2545348 <dbl>,
# GSM2545349 <dbl>, GSM2545350 <dbl>, GSM2545351 <dbl>, GSM2545352 <dbl>,
# GSM2545353 <dbl>, GSM2545354 <dbl>, GSM2545362 <dbl>, GSM2545363 <dbl>,
# GSM2545380 <dbl>Dplyr in action - write_csv
Finally, we could need to save our data as a new file for later use or sharing, we can use write_csv()
readxl::
readxl::is the Tidyverse library for reading data from Excel formatsread_excel(),read_xls()andread_xlsx()are some of the functions provided- The
excel_sheets()function yields the names of the sheets in the Excel file - But please, don’t use Excel
Any questions?
We will next talk about how to manipulate data in data frames/tibbles using the Tidyverse.
