09: Data visualization with ggplot2
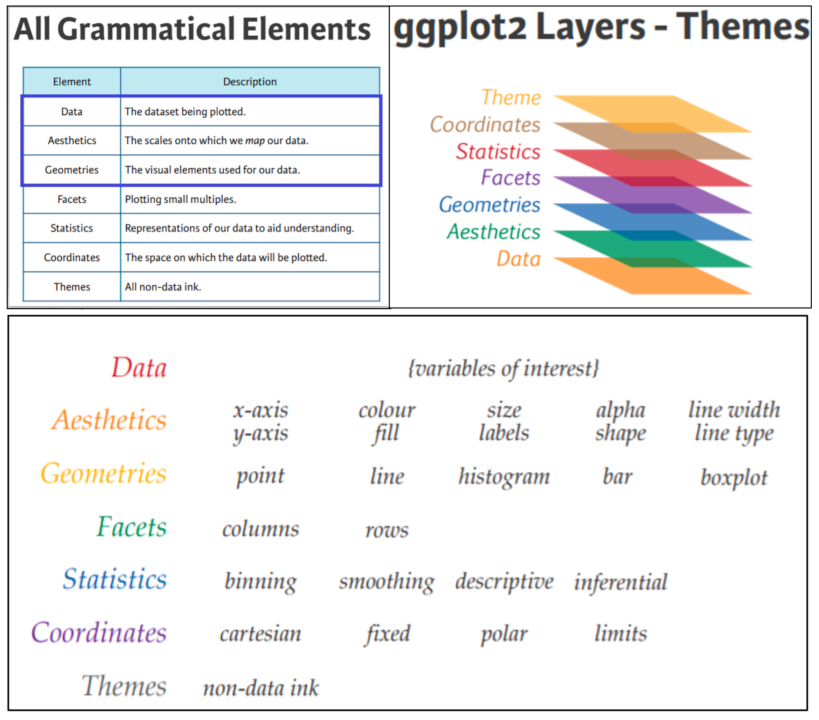
What is ggplot2?
- ggplot2 is part of the tidyverse, a set of packages created by Hadley Wickham.
- ggplot2 implements a grammar of graphics to enable creation of plots from modular building blocks
- ggplot2 is designed to work with tidy data (we’ll get into this later today).
Graph components
- Plots in ggplot2 consist of 3 main components:
- Data: The dataset being summarized
- Aesthetic mapping: Variables mapped to visual cues, such as x-axis and y-axis values and colors
- Geometry: The type of plot (scatterplot, boxplot, barplot, histogram, qqplot, smooth density, etc.)
ggplot(data = <DATA>, mapping = aes(<MAPPINGS>)) + <GEOM_FUNCTION>()
Graph components
geoms
geom_point() for scatter plots, dot plots, etc.geom_histogram() for histogramsgeom_boxplot() for, well, boxplots!geom_line() for trend lines, time series, etc.- and many more …
Graph components
- There are additional components:
- Scale
- Labels, Title, Legend
- Theme/Style
Graph components
![]()
Our dataset
Expression matrix from the mouse influenza experiment
library(tidyverse)
rnaseq_file = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/maxplanck-ie/Rintro/refs/heads/2025.04/qmd/data/rnaseq_counts_wide.csv"
rna = read_csv(rnaseq_file)
rna
# A tibble: 1,474 × 23
gene GSM2545336 GSM2545337 GSM2545338 GSM2545339 GSM2545340 GSM2545341
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Asl 1170 361 400 586 626 988
2 Apod 36194 10347 9173 10620 13021 29594
3 Cyp2d22 4060 1616 1603 1901 2171 3349
4 Klk6 287 629 641 578 448 195
5 Fcrls 85 233 244 237 180 38
6 Slc2a4 782 231 248 265 313 786
7 Exd2 1619 2288 2235 2513 2366 1359
8 Gjc2 288 595 568 551 310 146
9 Plp1 43217 101241 96534 58354 53126 27173
10 Gnb4 1071 1791 1867 1430 1355 798
# ℹ 1,464 more rows
# ℹ 16 more variables: GSM2545342 <dbl>, GSM2545343 <dbl>, GSM2545344 <dbl>,
# GSM2545345 <dbl>, GSM2545346 <dbl>, GSM2545347 <dbl>, GSM2545348 <dbl>,
# GSM2545349 <dbl>, GSM2545350 <dbl>, GSM2545351 <dbl>, GSM2545352 <dbl>,
# GSM2545353 <dbl>, GSM2545354 <dbl>, GSM2545362 <dbl>, GSM2545363 <dbl>,
# GSM2545380 <dbl>
Our dataset
Let’s plot a MA-like plot for GSM2545336 vs GSM2545380, first, we generate the tibble as:
# log2fc: M = log2(x/y) = log2(x) - log2(y)
# norm_mean: A = 1/2 ( log2(x) + log2(y) )
ma_data = rna %>%
select(gene, GSM2545336, GSM2545380) %>%
mutate(
norm_mean = ( log2(GSM2545336 + 1) + log2(GSM2545380 + 1) ) / 2,
log2fc = log2(GSM2545336 + 1) - log2(GSM2545380 + 1)
) %>%
select(gene, log2fc, norm_mean)
ma_data
# A tibble: 1,474 × 3
gene log2fc norm_mean
<chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Asl -0.0269 10.2
2 Apod -0.0759 15.2
3 Cyp2d22 0.0146 12.0
4 Klk6 0.148 8.10
5 Fcrls 0.318 6.27
6 Slc2a4 -0.0256 9.63
7 Exd2 -0.0653 10.7
8 Gjc2 0.136 8.11
9 Plp1 0.386 15.2
10 Gnb4 0.00810 10.1
# ℹ 1,464 more rows
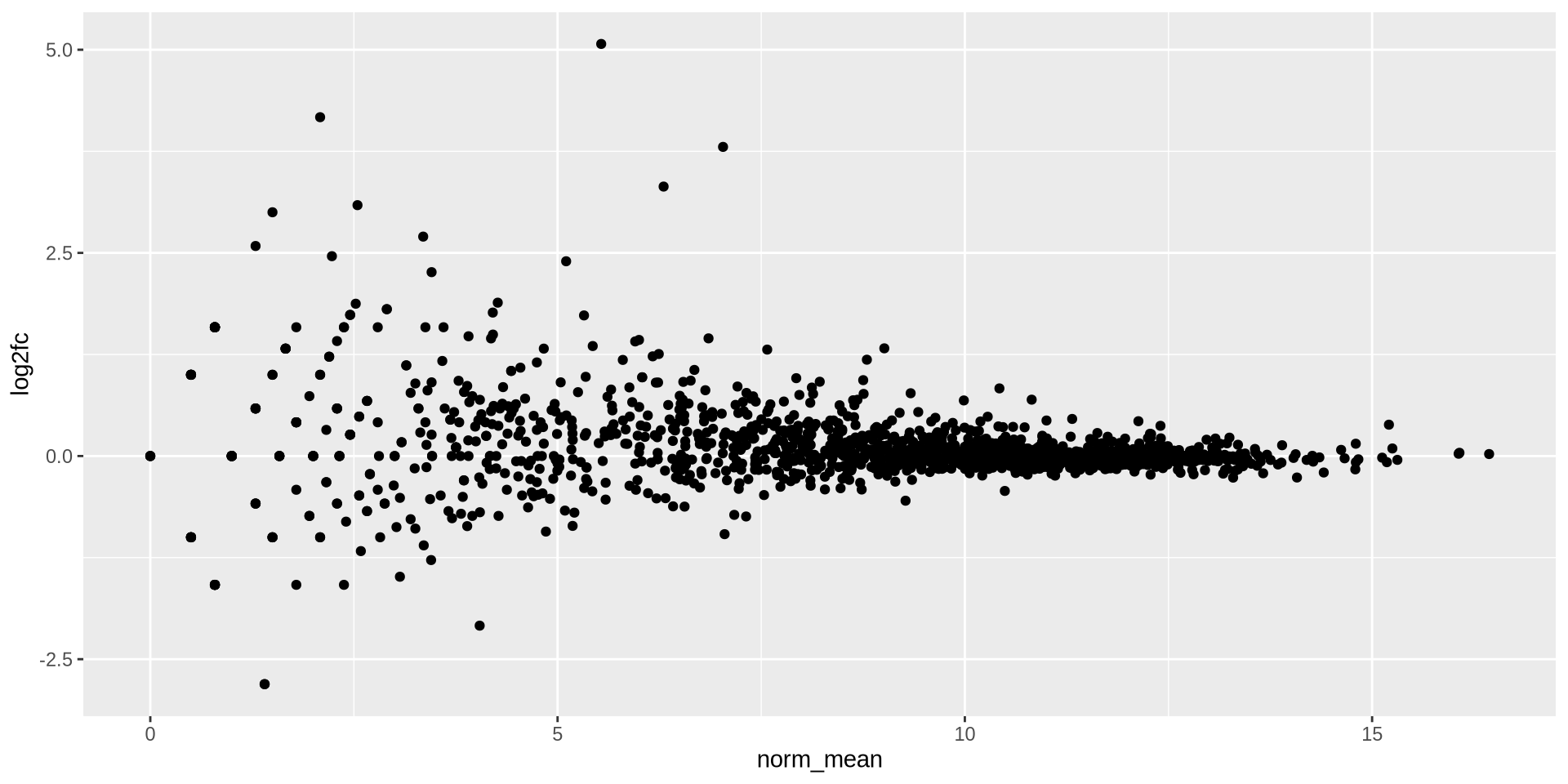
ggplot2 in action - geom_point()
geom_point() are basic scatter plots
ggplot(ma_data, aes(x = norm_mean, y = log2fc)) +
geom_point()
![]()
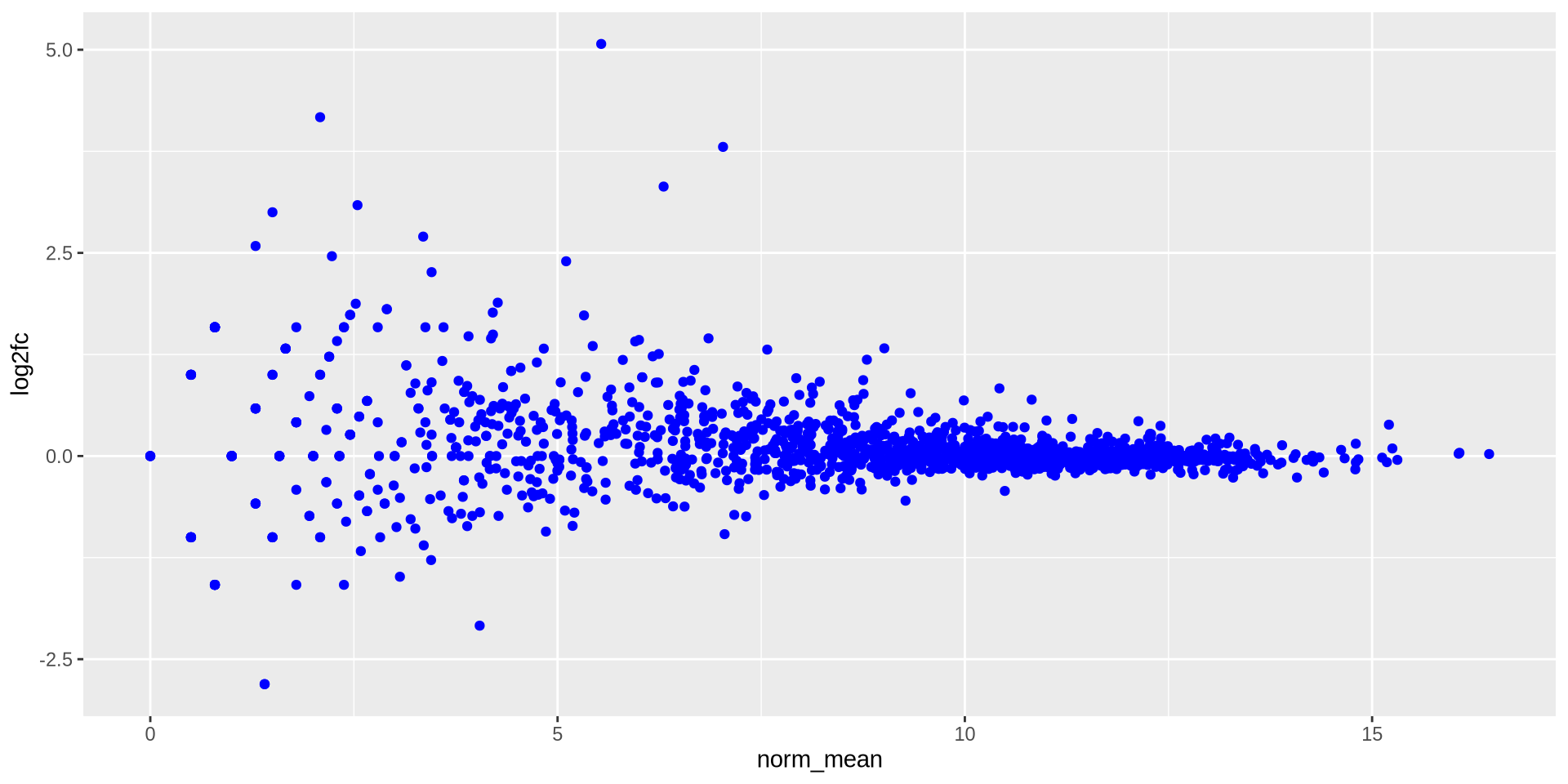
ggplot2 in action - geom_point()
We can modify graphic elements, for color
ggplot(ma_data, aes(x = norm_mean, y = log2fc)) +
geom_point(color = 'blue')
![]()
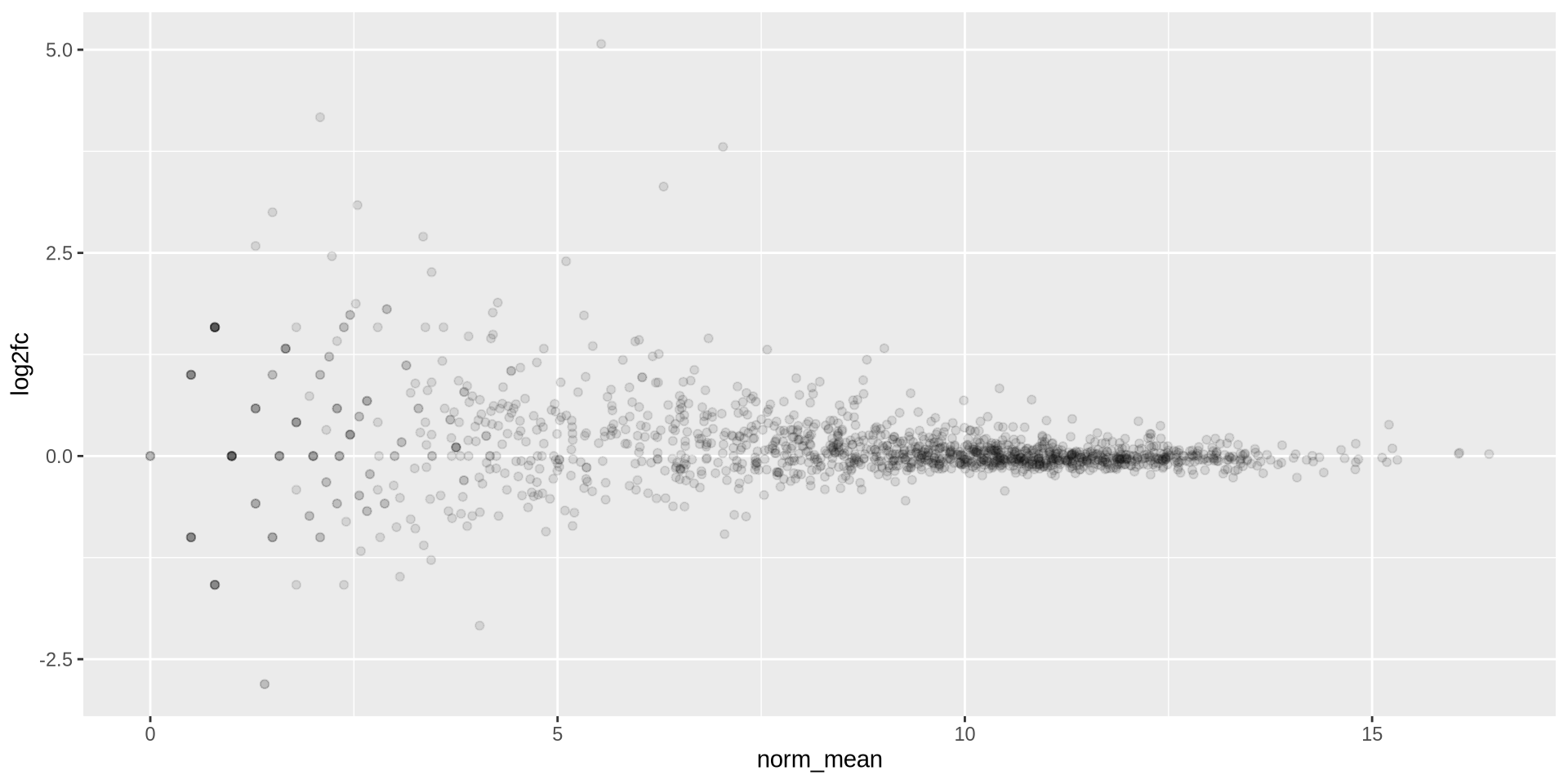
ggplot2 in action - geom_point()
Overplotting can be fixed using transparency with alpha
ggplot(ma_data, aes(x = norm_mean, y = log2fc)) +
geom_point(alpha = 0.1)
![]()
ggplot2 in action - geom_point()
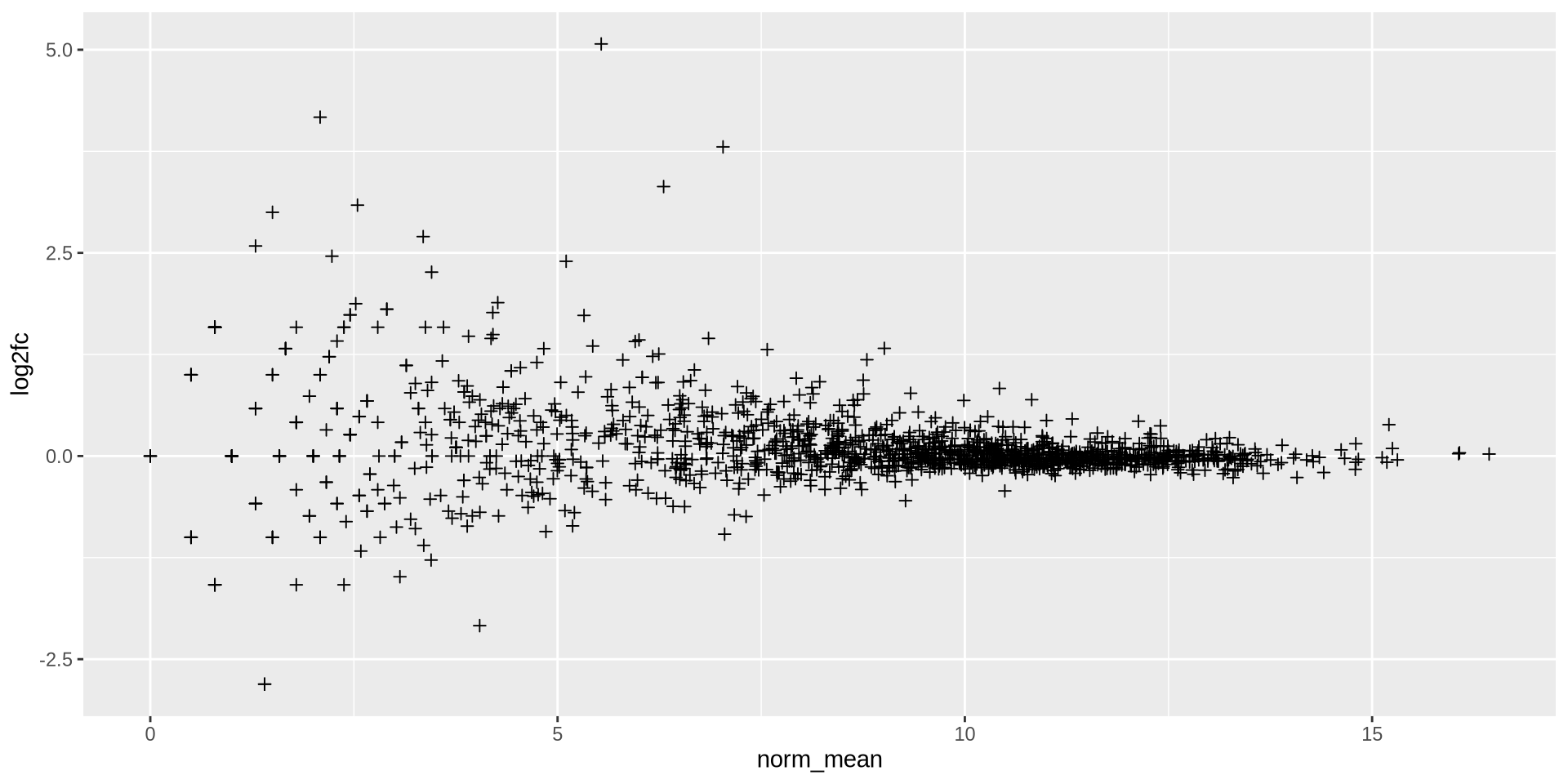
Point marks can be changed with shape, the numbers are predefined forms
ggplot(ma_data, aes(x = norm_mean, y = log2fc)) +
geom_point(shape = 3)
![]()
ggplot2 in action - geom_point()
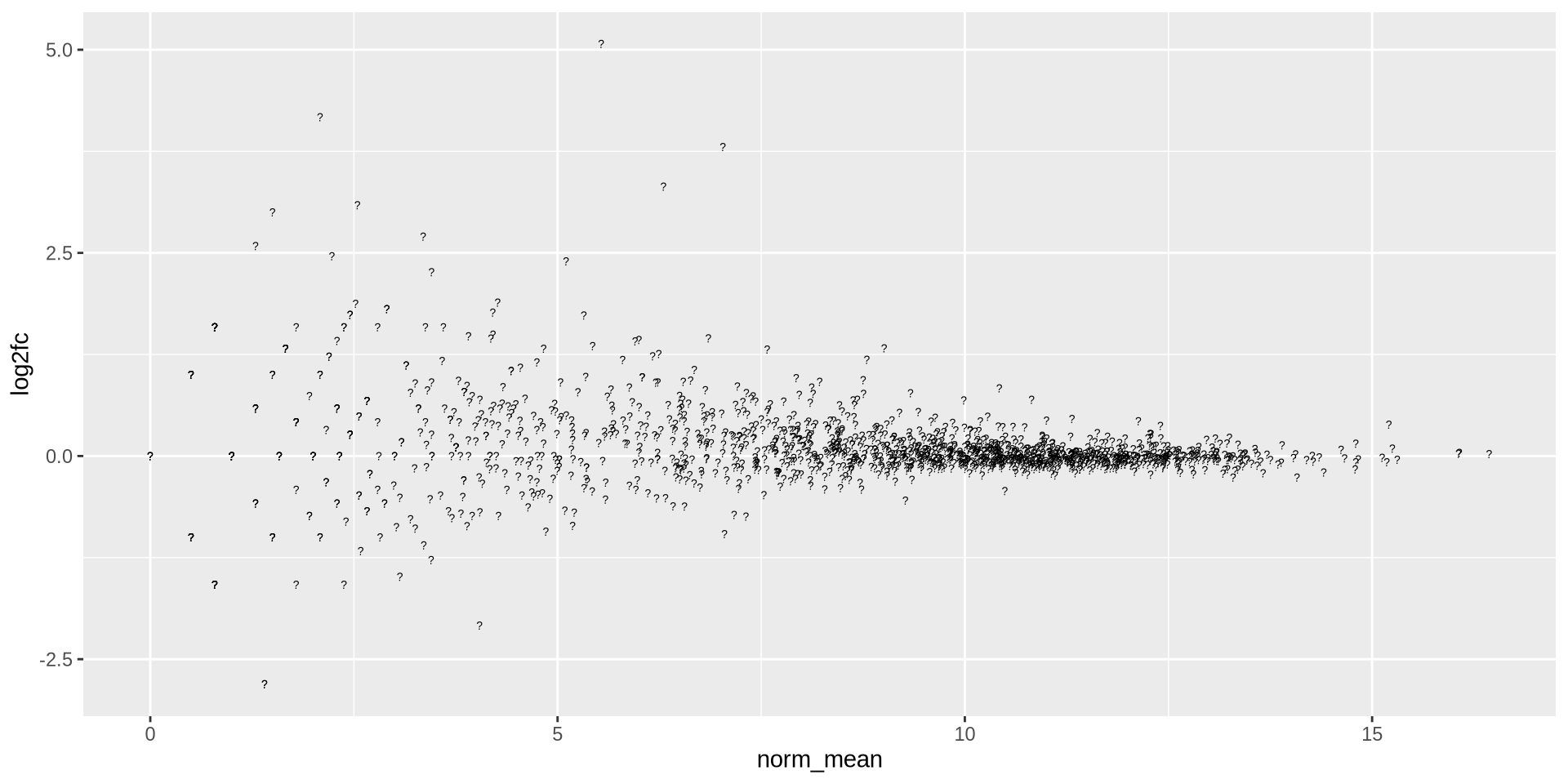
shape also accept any char
ggplot(ma_data, aes(x = norm_mean, y = log2fc)) +
geom_point(shape = '?')
![]()
ggplot2 in action - geom_point()
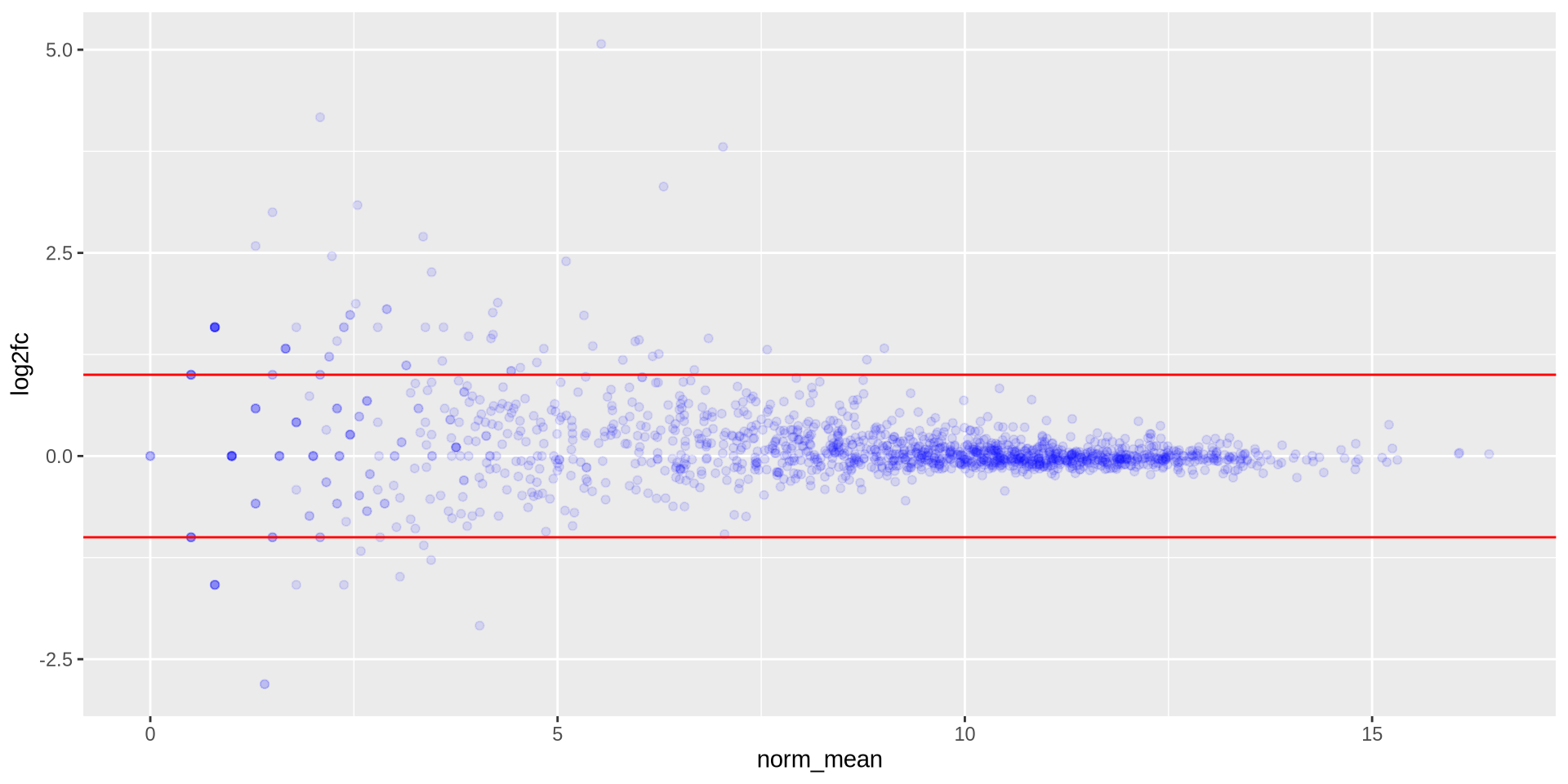
We can overlap new elements, such as an horizontal line geom_hline()
ggplot(ma_data, aes(x = norm_mean, y = log2fc)) +
geom_point(color = 'blue', alpha = 0.1) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 1, color = 'red') +
geom_hline(yintercept = -1, color = 'red')
![]()
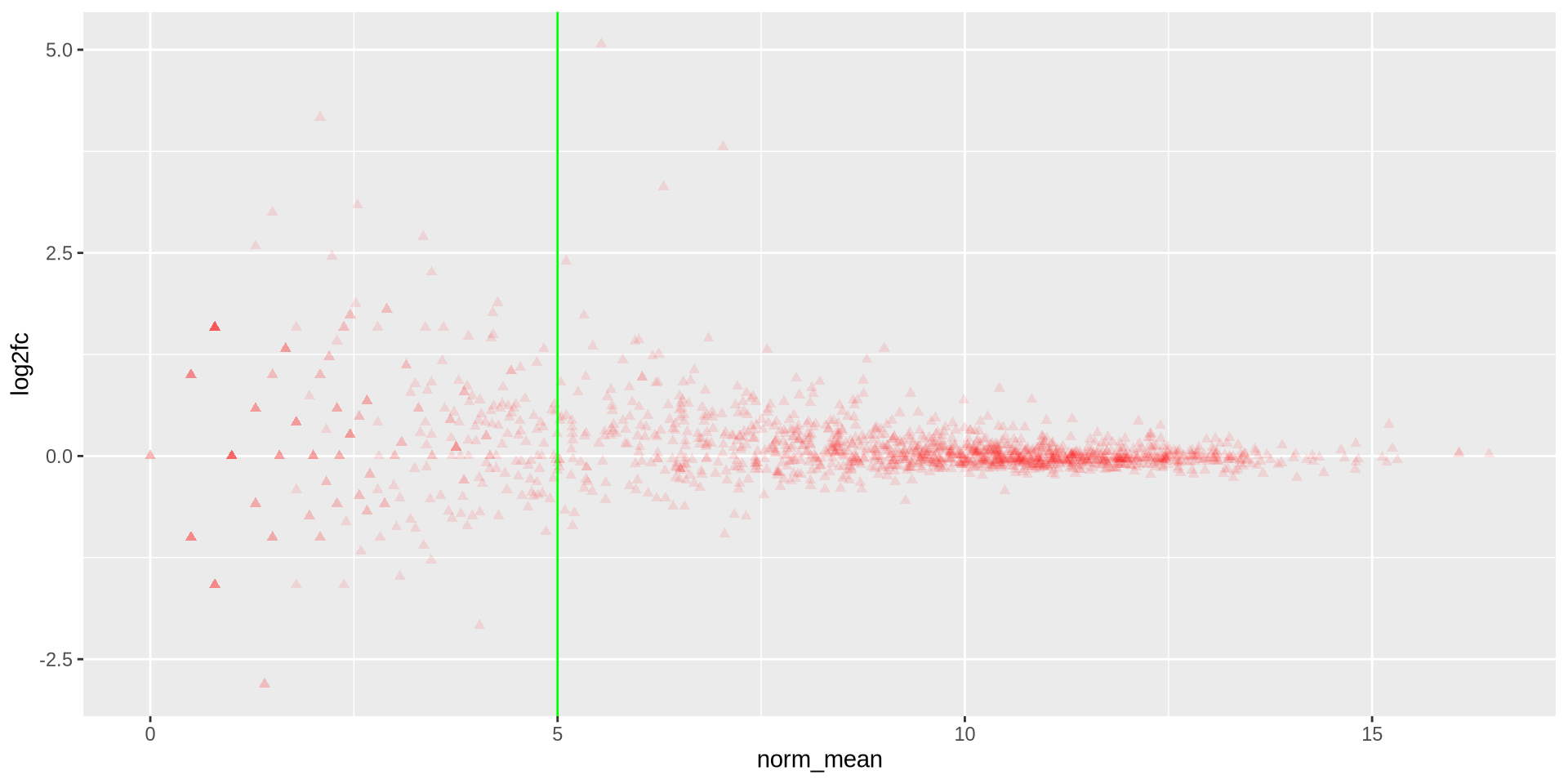
Hands on
Generate a similar plot comparing another 2 samples, use red “triangles” as points with a vertical green line in norm_mean = 5
Hands on
ggplot(ma_data, aes(x = norm_mean, y = log2fc)) +
geom_point(color = 'red', shape = 17, alpha = 0.1) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 5, color = 'green')
![]()
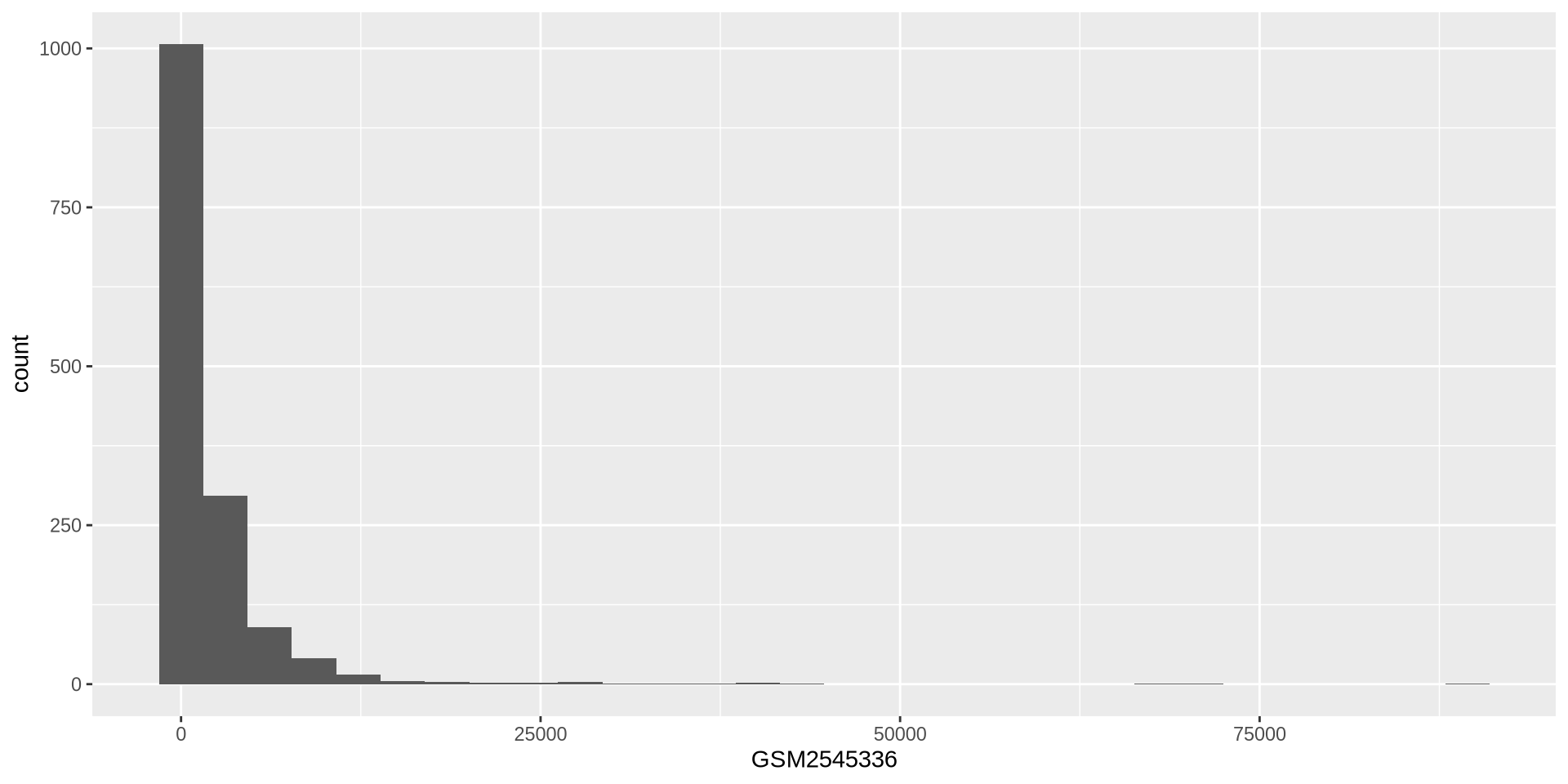
ggplot2 in action - geom_histogram()
Histogram of expression values for sample GSM2545336
ggplot(rna, aes(x = GSM2545336)) +
geom_histogram()
![]()
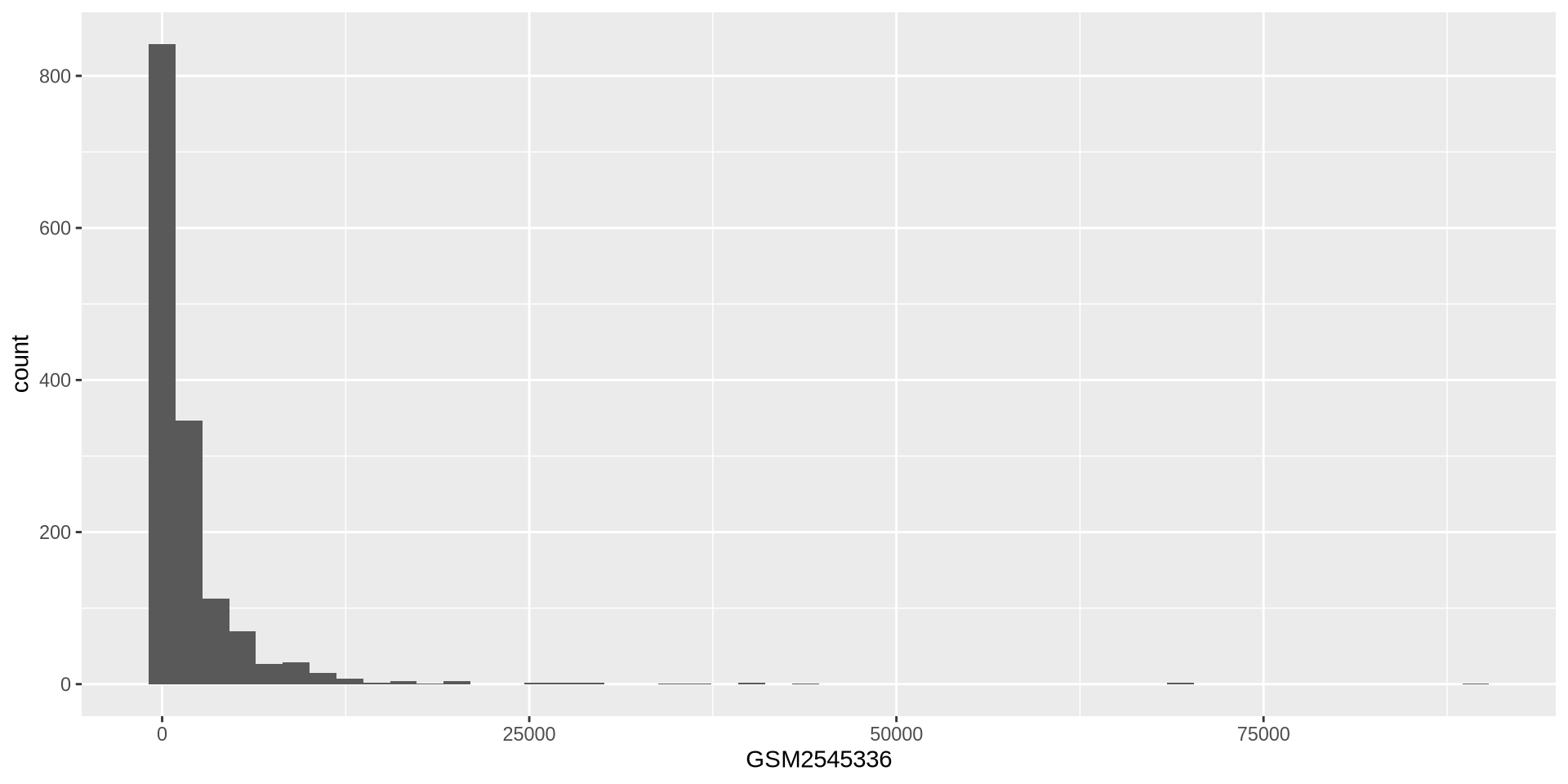
ggplot2 in action - geom_histogram()
We can adjust the histogram bins
ggplot(rna, aes(x = GSM2545336)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 50)
![]()
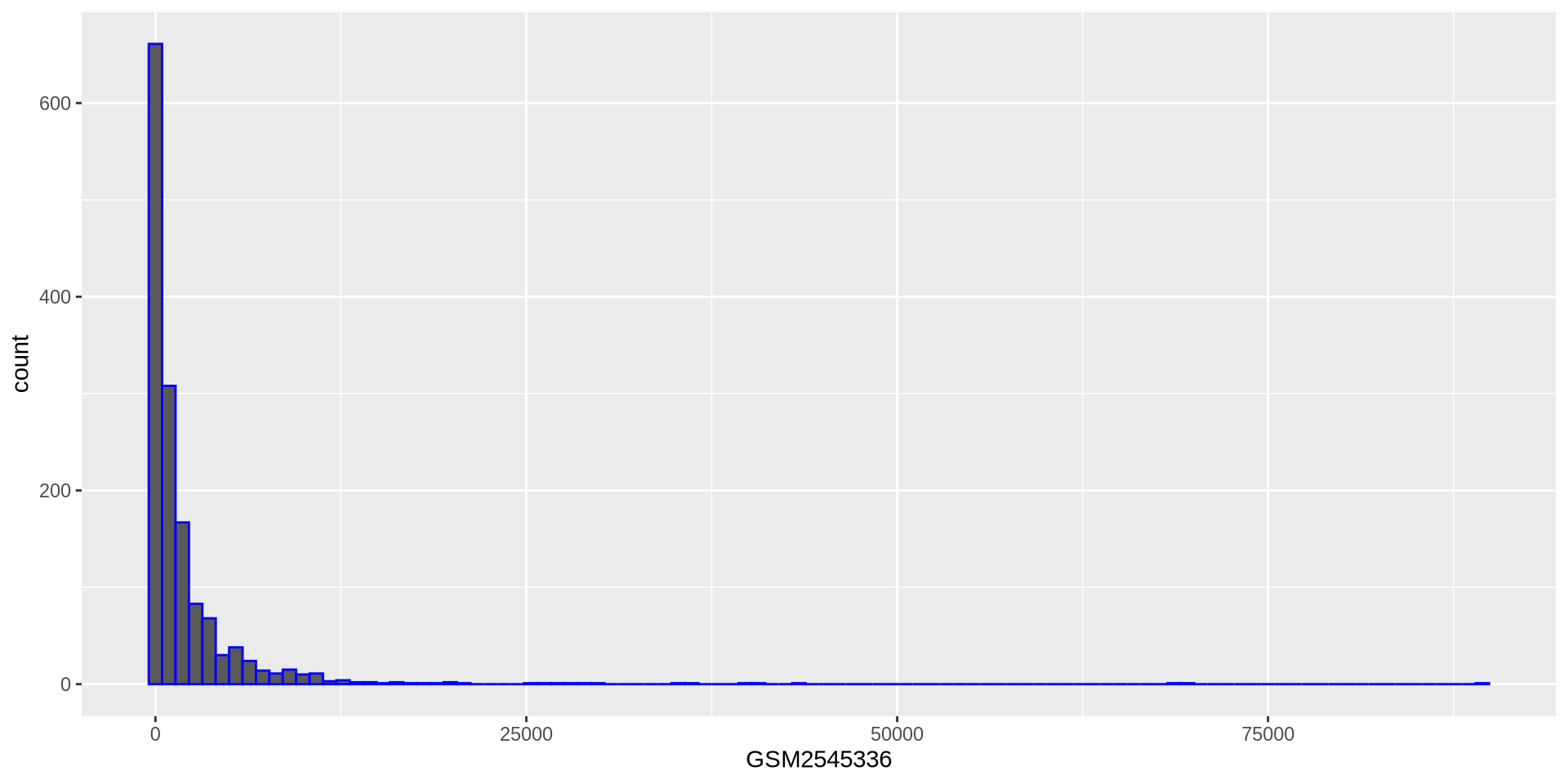
ggplot2 in action - geom_histogram()
We can use a variable to store a template
# Assign plot to a variable
hist_plot = ggplot(rna, aes(x = GSM2545336))
# Draw the plot
hist_plot + geom_histogram(bins = 100, color = 'blue')
![]()
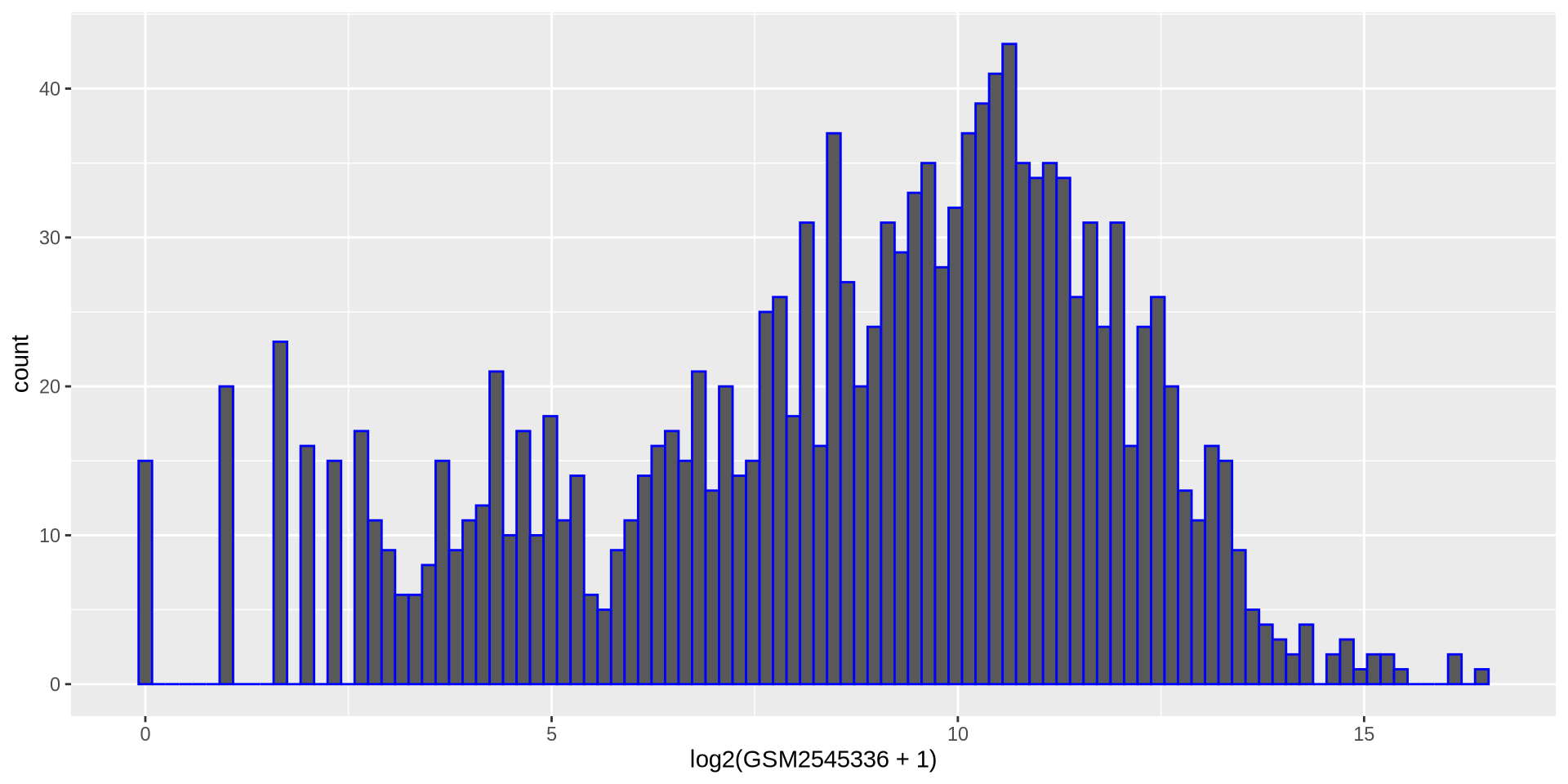
Hands on
Create a new histogram for another sample values but in log2 scale
Hands on
hist_plot = ggplot(rna, aes(x = log2(GSM2545336 + 1)))
hist_plot + geom_histogram(bins = 100, color = 'blue')
![]()
New dataset
rnaseq.csv is the long-format for the mouse influenza experiment. Let’s add a log2-expression column
rnaseq_file = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/maxplanck-ie/Rintro/refs/heads/2025.04/qmd/data/rnaseq.csv"
rna_data = read_csv(rnaseq_file)
rna_long = rna_data %>%
mutate(expression_log = log2(expression + 1))
rna_long
# A tibble: 32,428 × 20
gene sample expression organism age sex infection strain time tissue
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 Asl GSM254… 1170 Mus mus… 8 Fema… Influenz… C57BL… 8 Cereb…
2 Apod GSM254… 36194 Mus mus… 8 Fema… Influenz… C57BL… 8 Cereb…
3 Cyp2d22 GSM254… 4060 Mus mus… 8 Fema… Influenz… C57BL… 8 Cereb…
4 Klk6 GSM254… 287 Mus mus… 8 Fema… Influenz… C57BL… 8 Cereb…
5 Fcrls GSM254… 85 Mus mus… 8 Fema… Influenz… C57BL… 8 Cereb…
6 Slc2a4 GSM254… 782 Mus mus… 8 Fema… Influenz… C57BL… 8 Cereb…
7 Exd2 GSM254… 1619 Mus mus… 8 Fema… Influenz… C57BL… 8 Cereb…
8 Gjc2 GSM254… 288 Mus mus… 8 Fema… Influenz… C57BL… 8 Cereb…
9 Plp1 GSM254… 43217 Mus mus… 8 Fema… Influenz… C57BL… 8 Cereb…
10 Gnb4 GSM254… 1071 Mus mus… 8 Fema… Influenz… C57BL… 8 Cereb…
# ℹ 32,418 more rows
# ℹ 10 more variables: mouse <dbl>, ENTREZID <dbl>, product <chr>,
# ensembl_gene_id <chr>, external_synonym <chr>, chromosome_name <chr>,
# gene_biotype <chr>, phenotype_description <chr>,
# hsapiens_homolog_associated_gene_name <chr>, expression_log <dbl>
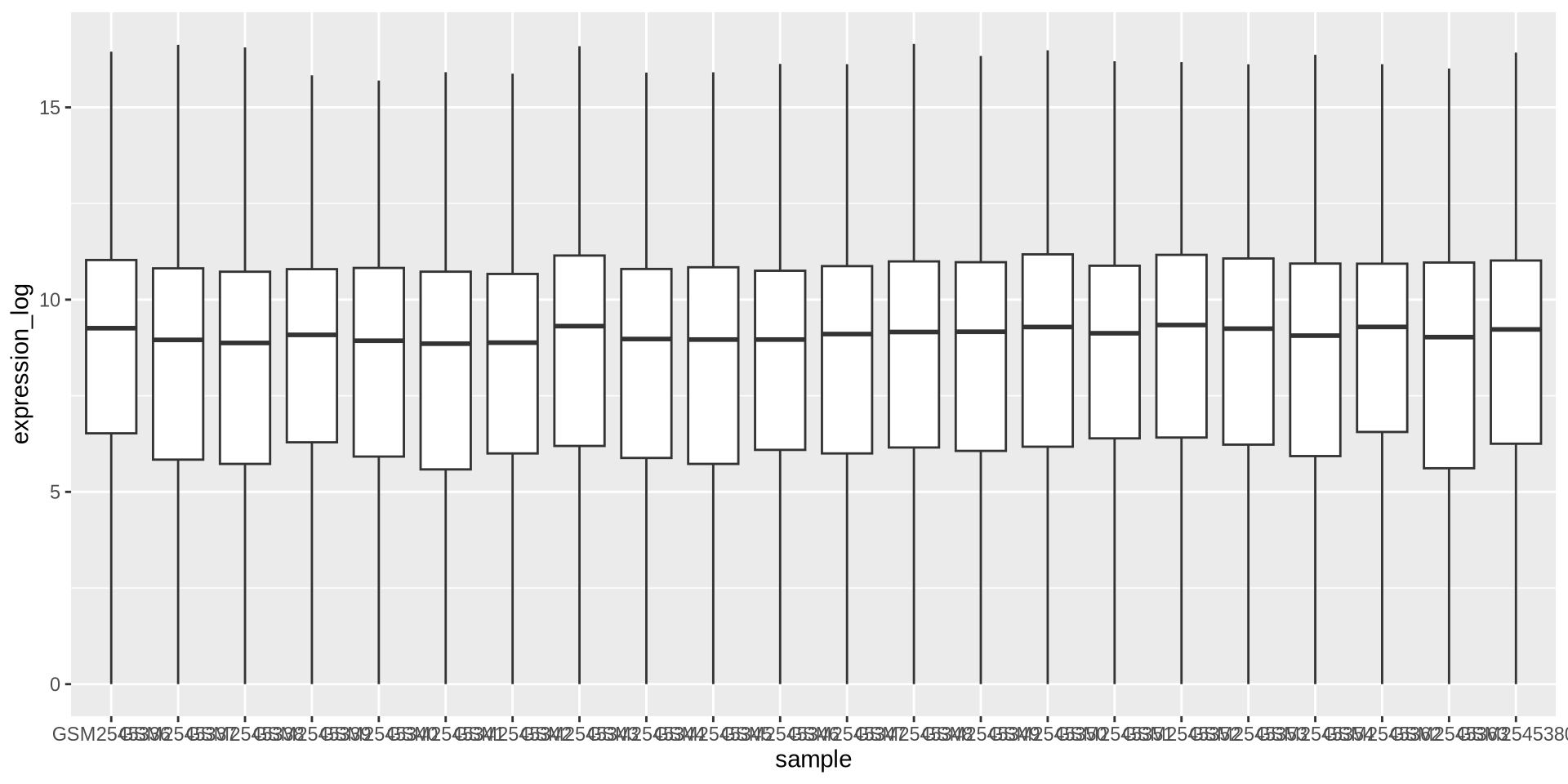
ggplot2 in action - geom_boxplot()
Boxplots are good to visualize distributions, let’s see gene log2-expression over samples
ggplot(rna_long, aes(y = expression_log, x = sample)) +
geom_boxplot()
![]()
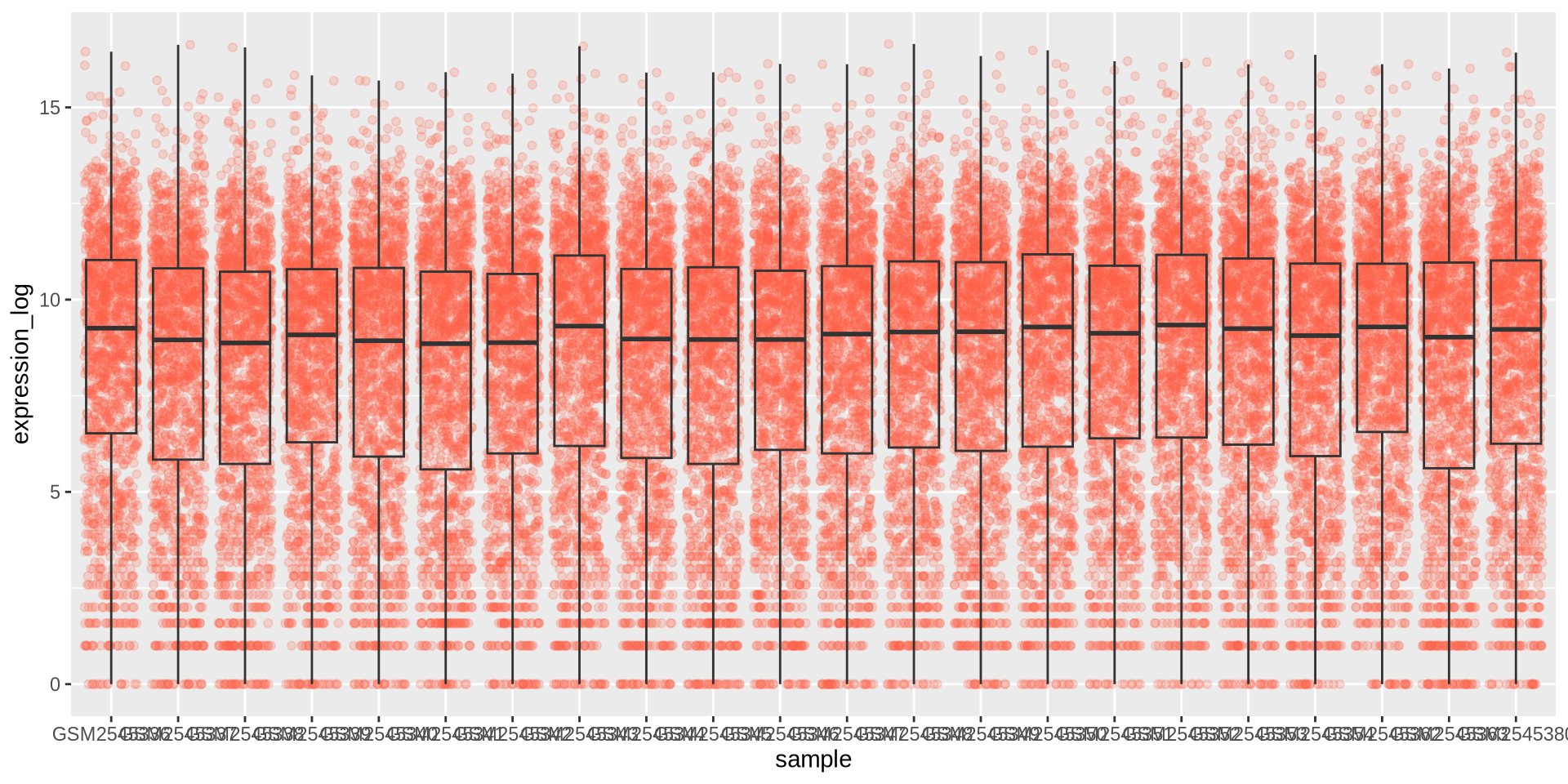
ggplot2 in action - geom_boxplot()
We can add the points over the boxplot with geom_jitter()
ggplot(rna_long, aes(y = expression_log, x = sample)) +
geom_jitter(alpha = 0.2, color = "tomato") +
geom_boxplot(alpha = 0)
![]()
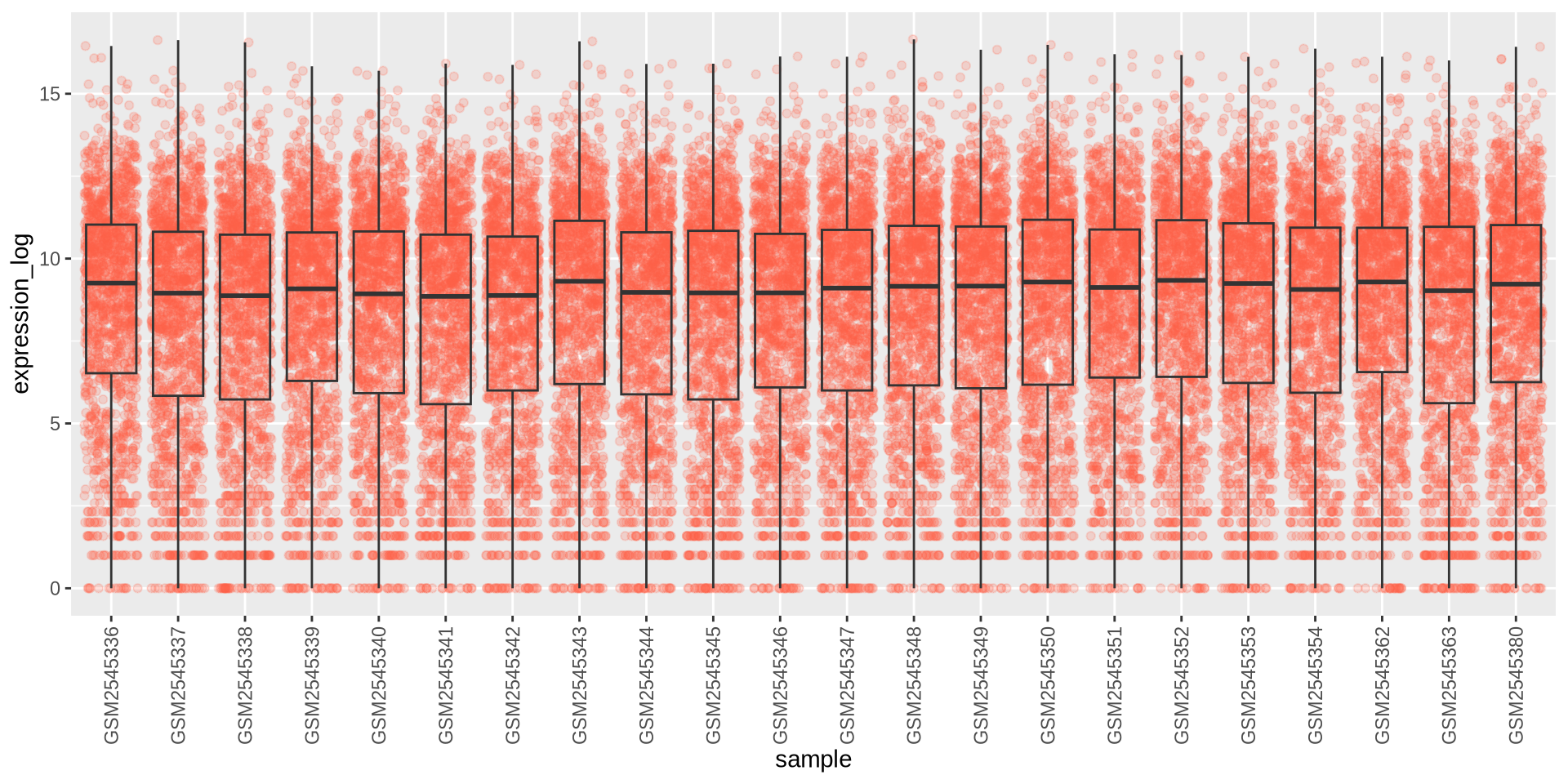
ggplot2 in action - geom_boxplot()
I can’t read the labels!! theme can modify the axis labels
ggplot(rna_long, aes(y = expression_log, x = sample)) +
geom_jitter(alpha = 0.2, color = "tomato") +
geom_boxplot(alpha = 0) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90, hjust = 0.5, vjust = 0.5))
![]()
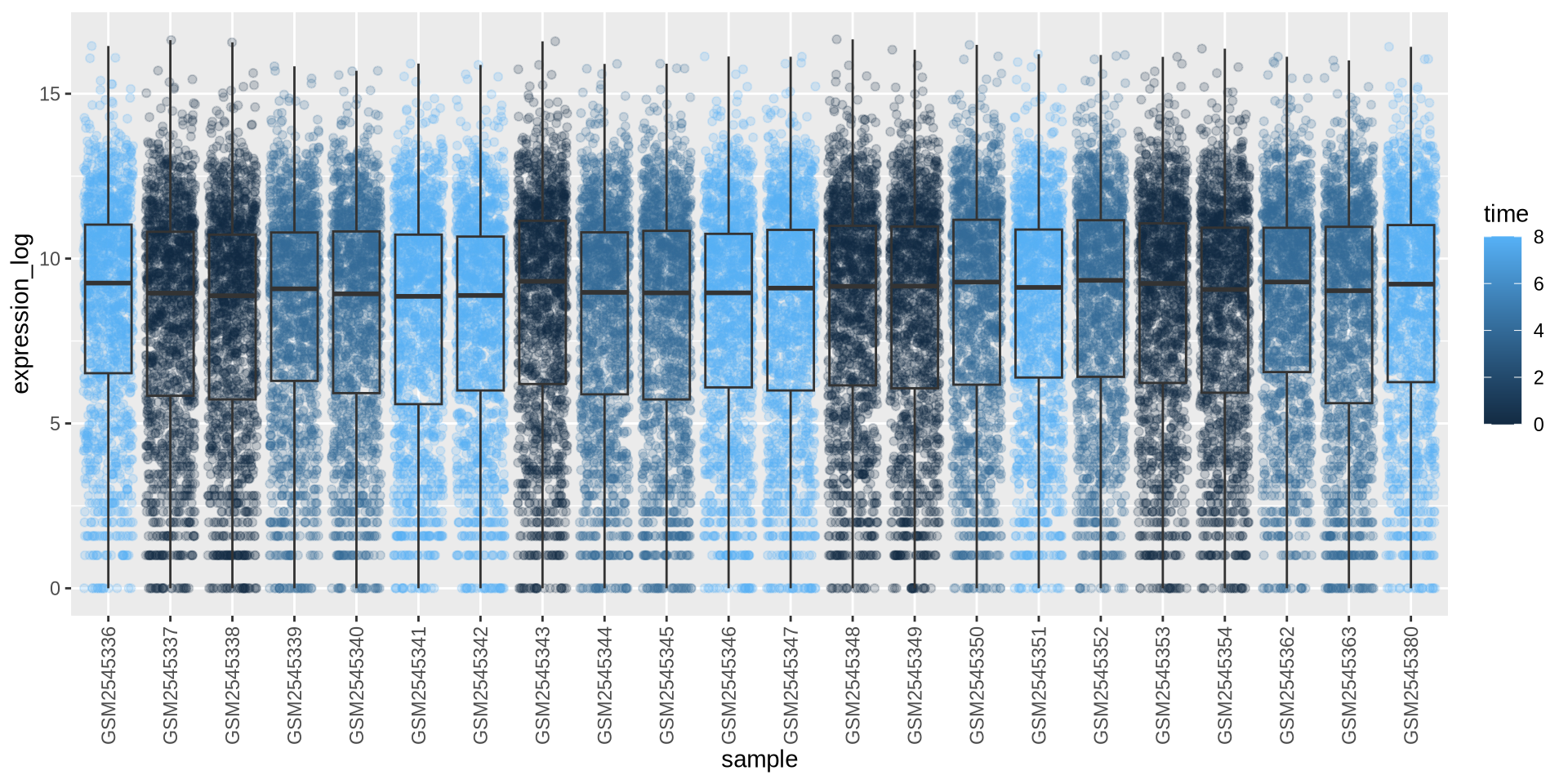
ggplot2 in action - geom_boxplot()
Can we color each sample per time point? Sure …
# time as integer
ggplot(rna_long, aes(y = expression_log, x = sample)) +
geom_jitter(alpha = 0.2, aes(color = time)) +
geom_boxplot(alpha = 0) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90, hjust = 0.5, vjust = 0.5))
![]()
Is this what we want?
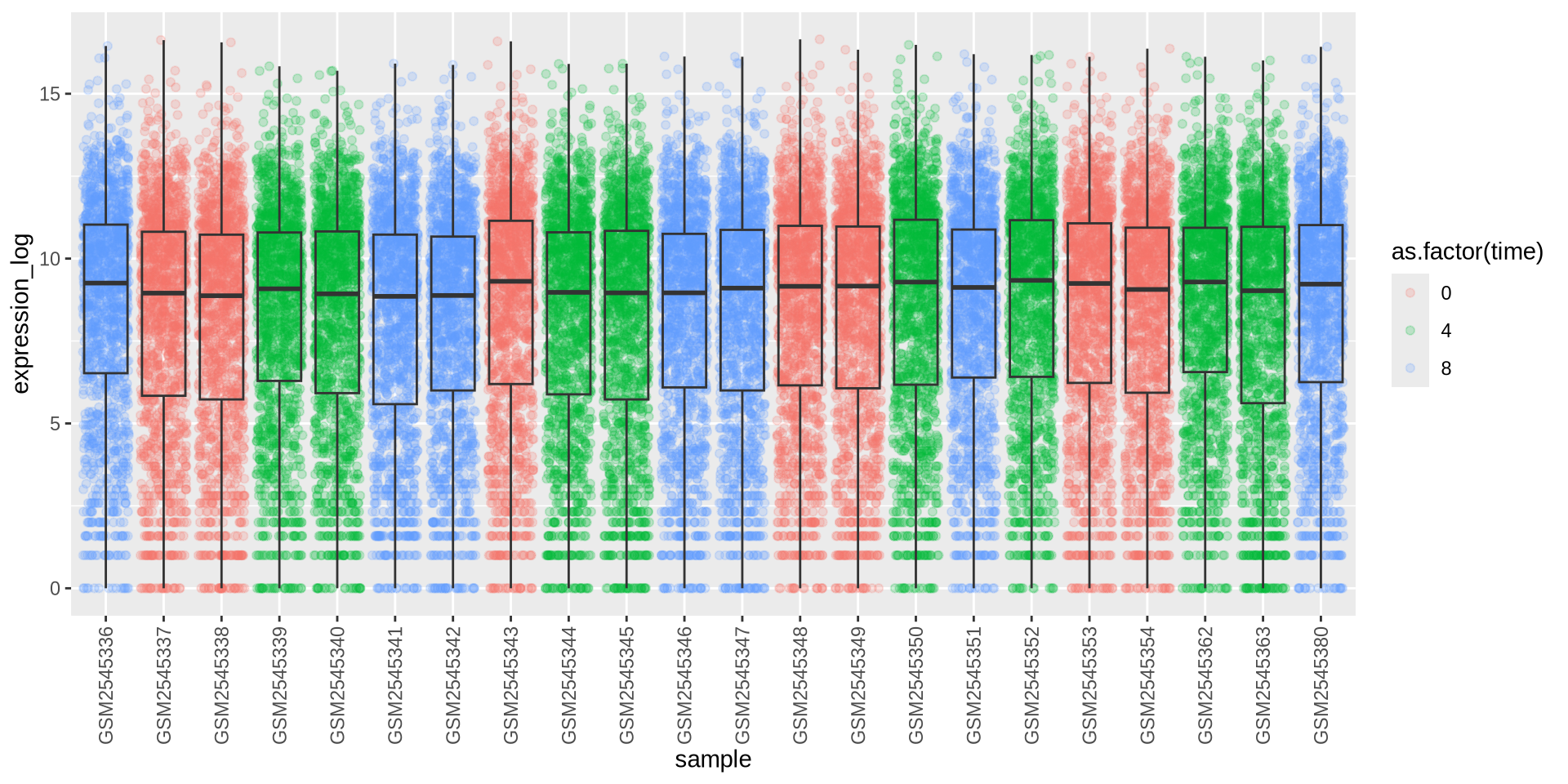
ggplot2 in action - geom_boxplot()
Can we color each sample per time point? Sure …
# time as factor
ggplot(rna_long, aes(y = expression_log, x = sample)) +
geom_jitter(alpha = 0.2, aes(color = as.factor(time))) +
geom_boxplot(alpha = 0) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90, hjust = 0.5, vjust = 0.5))
![]()
Better …
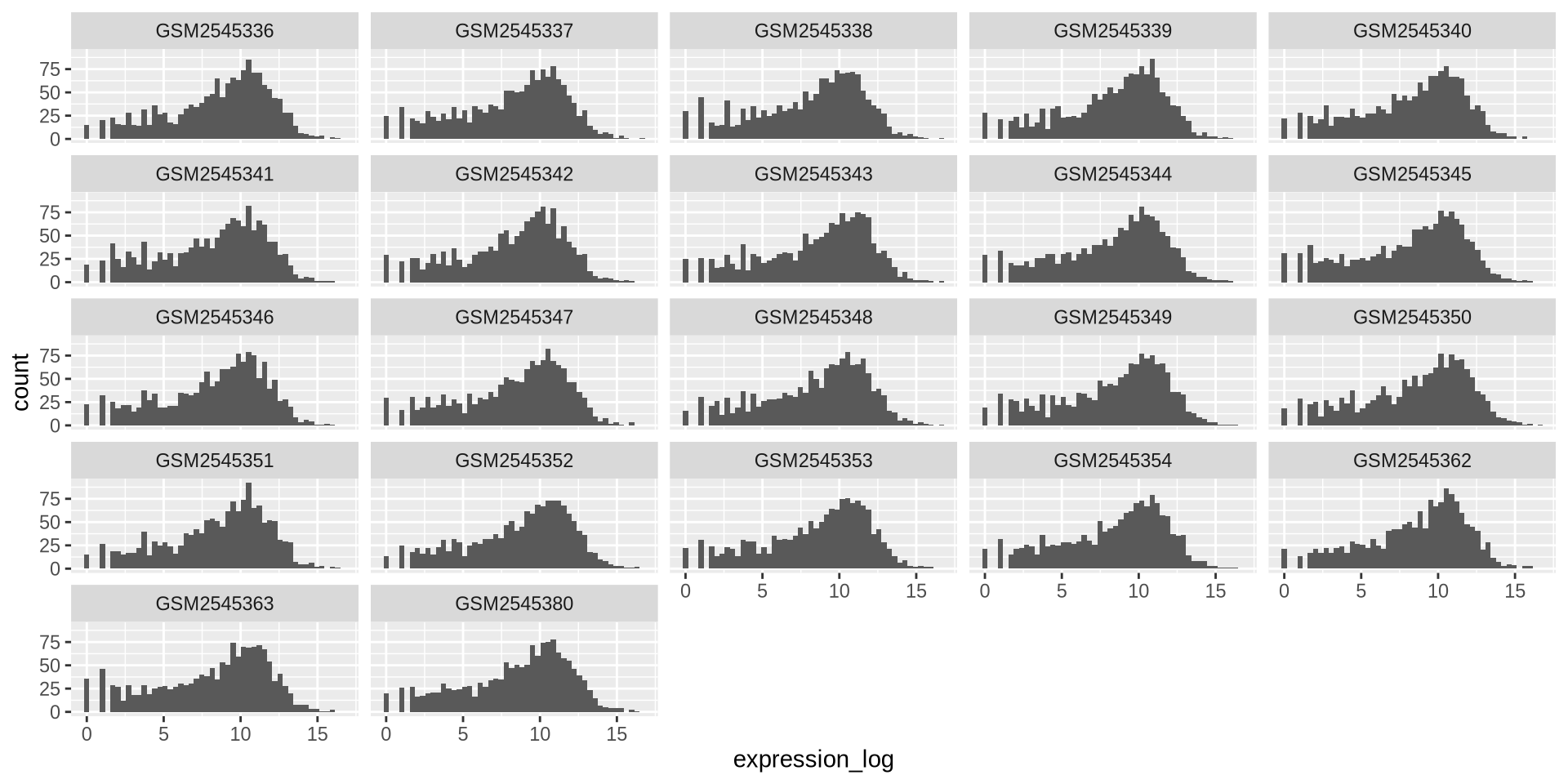
ggplot2 in action - facet_wrap()
We can plot multiple elements in a single plot separately with facet_wrap()
ggplot(rna_long,aes(x = expression_log)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 50) +
facet_wrap(~ sample)
![]()
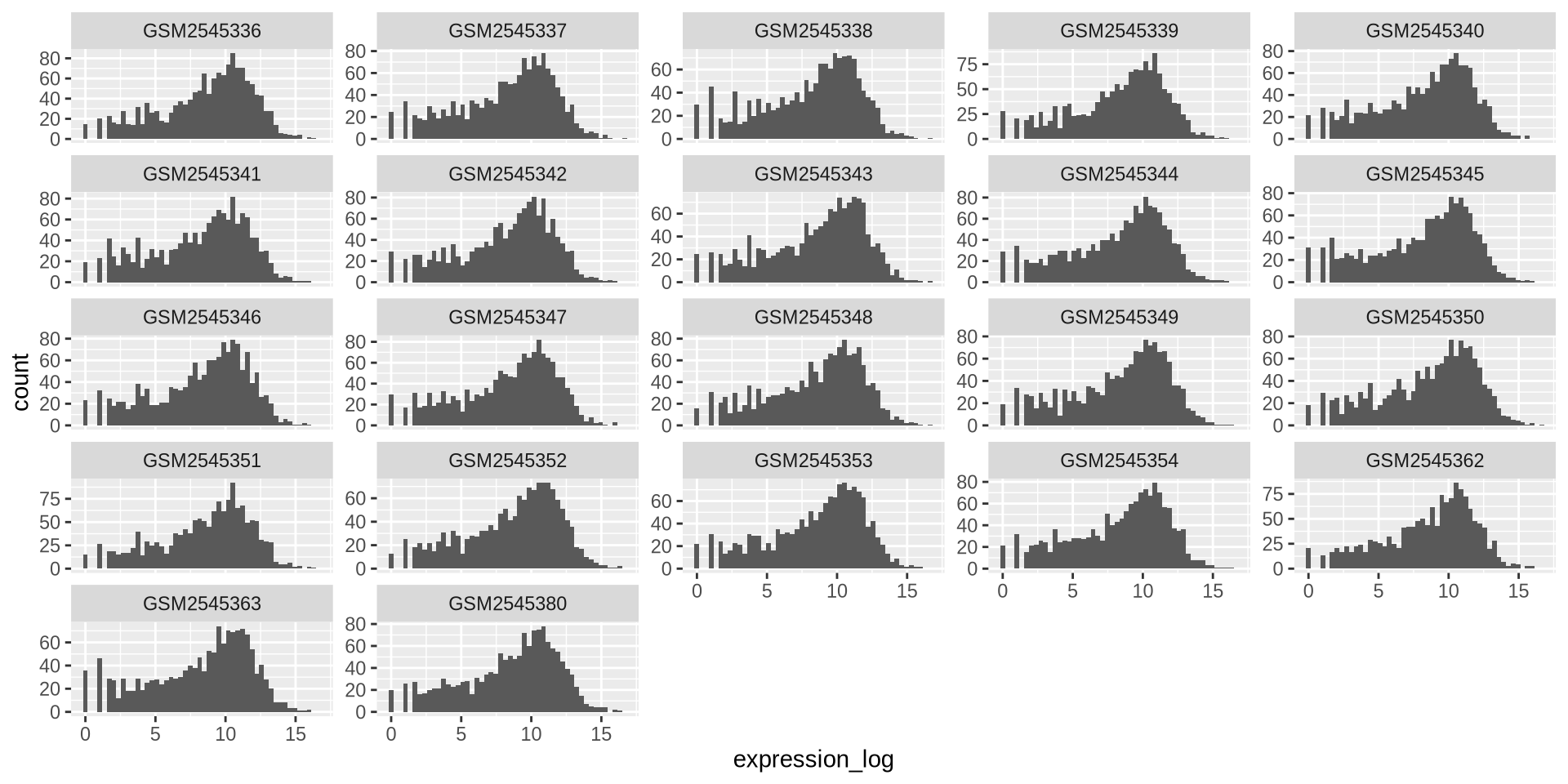
ggplot2 in action - facet_wrap()
By default, all scales are the same, to avoid this:
ggplot(rna_long, aes(x = expression_log)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 50) +
facet_wrap(~ sample, scales = "free_y")
![]()
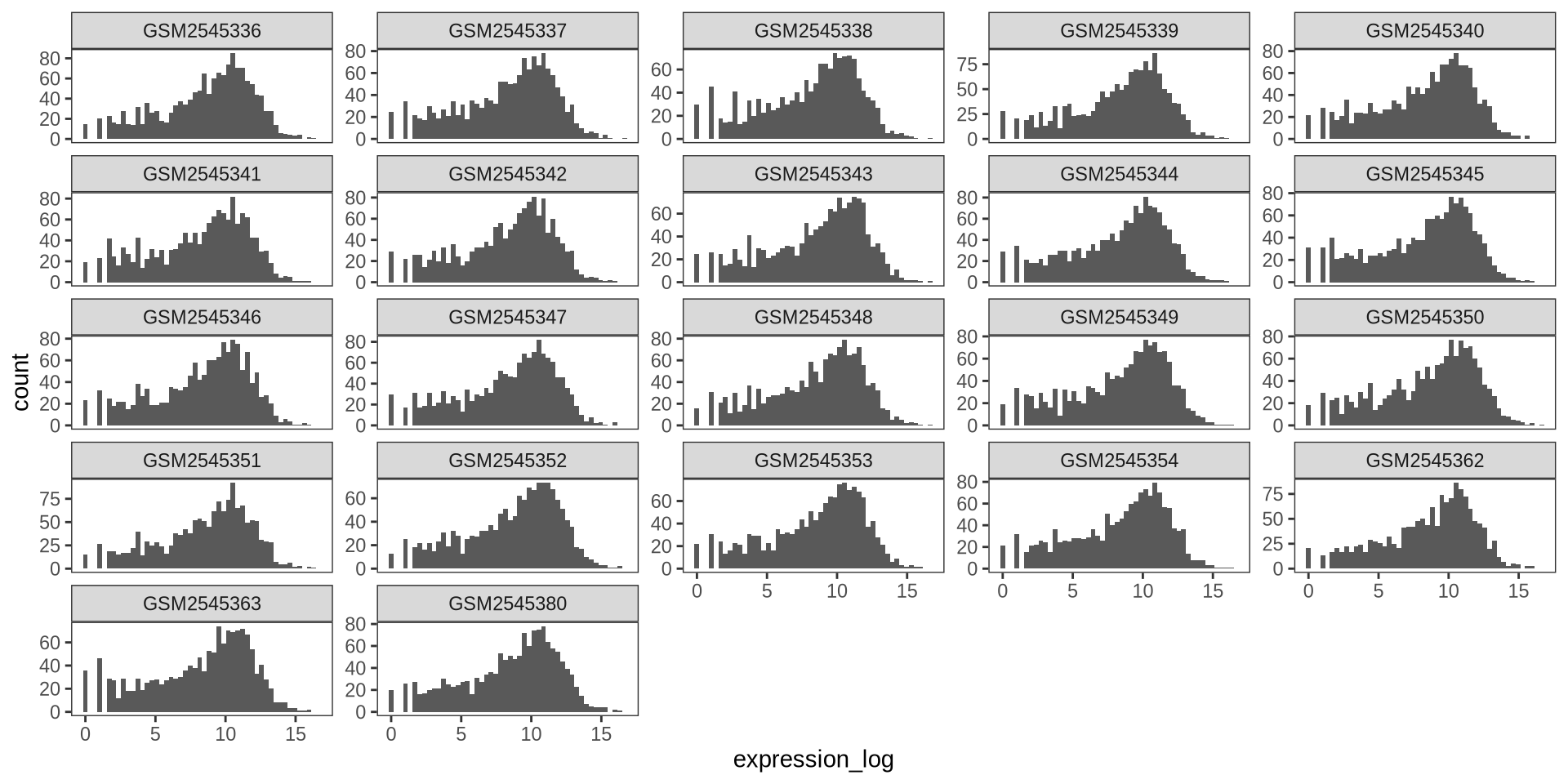
ggplot2 in action - theme_bw()
ggplot2 supports themes such as theme_bw()
ggplot(rna_long, aes(x = expression_log)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 50) +
facet_wrap(~ sample, scales = "free_y") +
theme_bw() +
theme(panel.grid = element_blank())
![]()
ggplot2 in action - ggsave()
At the end, we would like to save our gorgeous plot, we can use ggsave().
my_plot = ggplot(rna_long, aes(x = expression_log)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 50) +
facet_wrap(~ sample, scales = "free_y") +
theme_bw() +
theme(panel.grid = element_blank())
ggsave("samples_expr_histograms.png",
my_plot,
width = 15,
height = 10)
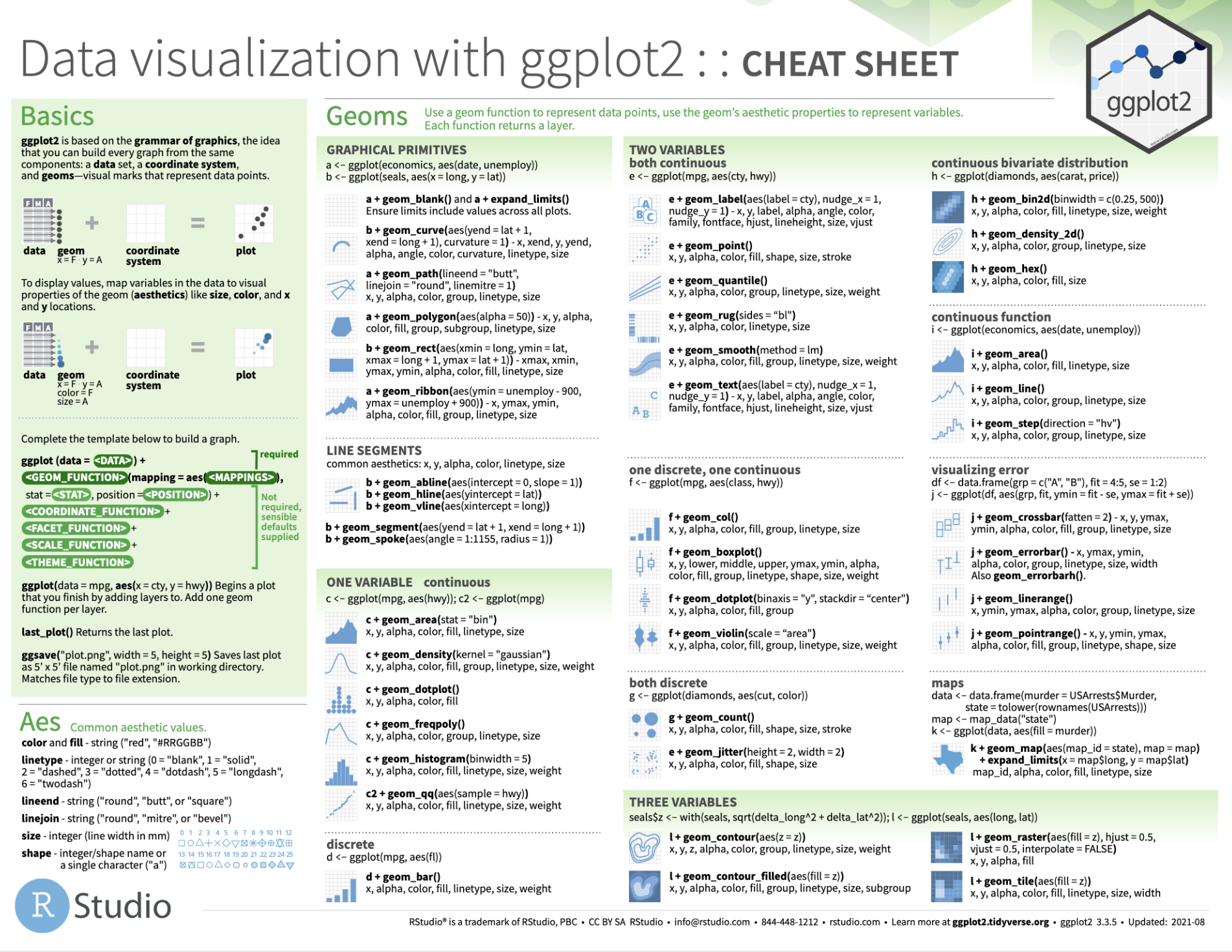
Tip of the iceberg
See this handy cheatsheet for lots more!
![]()
Any questions?
![]()